பாடத் தலைப்பு : அளவீடுகள் MEASUREMENTS
PDF டவுன்லோட் செய்ய : இந்த குறிப்புகள் அனைத்தையும் PDF வடிவில் டவுன்லோட் செய்துகொள்ள விரும்புபவர்கள், கீழே உள்ள தேர்வை ATTEND செய்யவும். தேர்வை முடிக்கும் பொழுது உங்களுடைய மதிப்பெண்ணுடன் PDF டவுன்லோட் செய்வதற்கான லிங்க்கும் காட்டப்படும். அதனைக் கிளிக் செய்து PDF டவுன்லோட் செய்து கொள்ளவும்.
இந்த இயலில் மொத்தம் 38 குறிப்புகளும் அவற்றைக் கொண்டு உருவாக்கப்பட்ட 45 கேள்விகளும் உள்ளன.
38 குறிப்புகளுக்கு கீழே தேர்வு உள்ளது
இந்தத் தேர்வு குறிப்புகள் குறித்த உங்களின் கருத்துக்களை கீழே உள்ள கமெண்ட் பாக்ஸில் தெரிவிக்கவும்
தேர்வு - கேள்விகளின் எண்ணிக்கை 45
வாழ்த்துகள். நீங்கள் இந்தத் தேர்வில் தேர்ச்சி பெற்றுள்ளீர் மீண்டும் இதே தேர்வினை எழுதுவதற்கு கீழே கிளிக் செய்யவும் அடுத்த தேர்விற்கு செல்ல கீழே கிளிக் செய்யவும் இந்தக் கேள்விகள் அனைத்தையும் PDF வடிவில் டவுன்லோட் செய்து கொள்ள விரும்புபவர்கள் கீழே கிளிக் செய்யவும் Tamil Medium Notes – Click here English Medium Notes – Click here இந்தக் கேள்விகள் உங்களுக்குப் பிடித்திருந்தால் எங்களைப் பாராட்டுவதற்கு கீழே உள்ள ஏதேனும் ஒரு விளம்பரத்தைக் கிளிக் செய்யவும். நீங்கள் இந்தத் தேர்வில் தேர்ச்சி பெறுவதற்கான மதிப்பெண்களைப் பெறவில்லை. மீண்டும் இதே தேர்வினை எழுதுவதற்கு கீழே கிளிக் செய்யவும் அடுத்த தேர்விற்கு செல்ல கீழே கிளிக் செய்யவும் இந்தக் கேள்விகள் அனைத்தையும் PDF வடிவில் டவுன்லோட் செய்து கொள்ள விரும்புபவர்கள் கீழே கிளிக் செய்யவும் Tamil Medium Notes – Click here English Medium Notes – Click here இந்தக் கேள்விகள் உங்களுக்குப் பிடித்திருந்தால் எங்களைப் பாராட்டுவதற்கு கீழே உள்ள ஏதேனும் ஒரு விளம்பரத்தைக் கிளிக் செய்யவும்.
click to copy shortcodeResults
#1. ஒரு பொருளின் தோற்ற நிலையை இருவேறு பார்வை கோடுகளின் வழியே நோக்கும் போது ஏற்படுவதாக தோன்றும் அளவீட்டு மாறுபாடு அல்லது அளவீட்டு இடப்பெயர்ச்சி எவ்வாறு அழைக்கப்படுகிறது Displacement or difference in the apparent position of an object viewed along two different lines of site is called as
#2. மிகப்பெரிய அளவிலான எடையை அளவிட உதவும் அளவு Bigger weights are measured in
#3. ஒரு பொருளின் எடை பூமியில் மற்றும் நிலவில் உள்ள வேறுபாடு The difference between, weight of an object in Earth and moon
#4. கருத்து 1 :திரவங்களையும் வாயுக்களையும் நீளத்தைப் போல கன மீட்டரிலும் அளவீடு செய்யலாம் Statement 1:SLiquids and gases are also can be measured in cubic metre. கருத்து 2: மிகப்பெரிய அளவிலான எடையை டன் அல்லது மெட்ரிக் டன் அளவில் அளவிடலாம். Statement 2:Bigger weights are measured in tonne or Metric Tonne.
#5. வாகனங்கள் கடக்கும் தொலைவை கணக்கிட பயன்படும் கருவி device used for indicating distance travelled by an automobile
தேர்வு எழுதி முடிக்கும் பொழுது உங்களுடைய மதிப்பெண் மற்றும் PDF டவுன்லோட் செய்வதற்கான லிங்க் காட்டப்படும்
வரி வரியாகப் படித்து எடுக்கப்பட்ட ஒரு வரி குறிப்புகள்
- தெரிந்த ஒரு அளவைக் கொண்டு தெரியாத அளவை ஒப்பிடுவது "அளவீடு" எனப்படும்.
- அளவீடு என்பது எண் மதிப்பு மற்றும் அலகு என இரண்டு பகுதிகளைக் கொண்டது.
- ஏதேனும் இரு புள்ளிகளுக்கு இடையே உள்ள தூரம் நீளம் எனப்படும்
- நீளத்தின் அலகு மீட்டர். அதன் குறியீடு மீ(m) என குறிக்கப்படுகிறது
- நீளத்தின் மிகச்சிறிய அளவீடுகள் மில்லி மீட்டர் மற்றும் சென்டி மீட்டரில் குறிக்கப்படுகின்றன.
- நீளத்தின் மிகப்பெரிய அளவீடுகள் மீட்டர் மற்றும் கிலோமீட்டரில் குறிக்கப்படுகின்றன
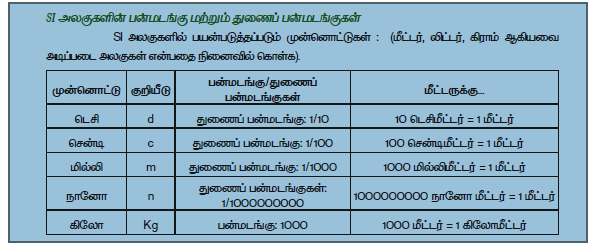
- ஒரே மாதிரியான அளவீட்டு முறைக்காக, உலகம் முழுவதும் உள்ள அறிவியல் அறிஞர்கள் பொதுவான அலகுகளை ஏற்றுக்கொண்டனர். இந்த முறையானது பன்னாட்டு அலகு முறை அல்லது SI அலகு முறை எனப்படுகிறது.
- ஒரு பொருளின் தோற்ற நிலையை இரு வேறு பார்வைக் கோடுகளின் வழியே நோக்கும்போது ஏற்படுவதாக தோன்றும் அளவீட்டு மாறுபாடு அல்லது அளவீட்டு இடப்பெயர்ச்சியே இடமாறு தோற்றப்பிழை எனப்படும்
- நீளம், அகலம் என்ற இருவகையான நீளங்களை பயன்படுத்தி பரப்பை கணக்கிடலாம்
- பரப்பளவு= நீளம்×அகலம்
- பருமன் என்பது வழி அலகு ஆகும்.
- ஒரு பெட்டியின் பருமன் = நீளம்×அகலம்×உயரம்
- திரவங்களுக்கு நிலையான வடிவம் இல்லை. அவை கொள்கலனின் வடிவத்தை எடுத்துக் கொள்ளும்.
- அளவுகள் குறிக்கப்பெற்ற கொள்கலன்கள், குடுவைகள், பிப்பெட்டுகள், பியூரெட்டுகள் போன்றவை ஒரு திரவத்தின் பருமனை மிகச் சரியாக அளவிட உதவுகின்றன.
- திரவத்தின் பருமனானது பொதுவாக லிட்டரில் அளவிடப்படுகிறது.
- ஒரு பருப்பொருள் எவ்வளவு இடத்தை அடைத்துக் கொள்கிறதோ அதுவே அதன் பருமனாகும்
- 1 மில்லி லிட்டர் = 1 கன சென்டிமீட்டர் அல்லது 1 செ.மீ3
- வாயுக்கள் தான் அடைத்து வைக்கப்பட்ட கொள்கலனின் முழு கொள்ளளவையும் அடைத்துக் கொள்ளும் திறன் கொண்டவை.
- அதிக கொள்ளளவு கொண்ட கலனில் உள்ள வாயுவை அதிக அழுத்தத்தைக் கொடுத்து சிறிய கொள்ளளவு கொண்ட கலனிலும் அடைக்கலாம்.
- திடப் பொருட்களின் பருமன் SI அலகு முறையில் கனமீட்டர் அல்லது மீ3 ஆகும்.
- திரவங்களும் வாயுக்களும் பொதுவாக லிட்டரில் அளவிடப்படுகிறது
- திரவங்களையும் வாயுக்களையும் நீளத்தைப் போல மீ3 அல்லது கன மீட்டரிலும் அளவீடு செய்யலாம்.
- நிறை என்பது ஒரு பொருளில் உள்ள பருப்பொருளின் அளவு ஆகும்.
- எடை என்பது நிறையின் மேல் செயல்படும் புவியீர்ப்பு விசை ஆகும்.
- நிறையின் எஸ்ஐ அலகு கிலோ கிராம்
- மிகப்பெரிய அளவிலான எடையை டன் அல்லது மெட்ரிக் டன் அளவில் அளவிடலாம்.
- ஒரு தெரிந்த நிலையான நிறையோடு ஒரு தெரியாத பொருளின் நிறையை ஒப்பிடுவதன் மூலம் அந்தப் பொருளின் நிறையானது கணக்கிடப்படுகிறது. அது படித்தர நிறை என்றும் அழைக்கப்படுகிறது.
- துல்லியமான எடையைக் காண மின்னணு தராசு என்ற கருவி பயன்படுகிறது.
- ஆய்வகங்களில் பரிசோதனைகளைச் செய்ய பொதுவாக மின்னணு தராசை பயன்படுத்தி வேதிப்பொருட்களின் எடையை மிகத்துல்லியமாக அளவிடுகின்றனர்.
- மூன்று வகையான பிழைகளை தவிர்ப்பதன் மூலம் அளவுகோலை பயன்படுத்தும்போது துல்லியமான அளவுகளை அளக்கலாம்.
- ஒழுங்கற்ற பொருட்களின் பருமனை அளந்தறிய நீர் இடப்பெயர்ச்சி முறை பயன்படுகிறது.
1 சென்டிமீட்டர் = 10 மில்லி மீட்டர்
1 மீட்டர் = 100 சென்டிமீட்டர்
1 கிலோ மீட்டர் = 1000 மீட்டர்
1 கிலோமீட்டர் = 100000 சென்டிமீட்டர்
1000 மில்லி கிராம் = 1 கிராம்
1000 கிராம் = 1 கிலோ கிராம்
1000 கிலோ கிராம் = 1 டன்
நீளத்தின் SI அலகு மீட்டர்
நிறையின் SI அலகு கிலோகிராம்
காலத்தின் SI அலகு வினாடி
பரப்பளவின் SI அலகு மீ2
பருமனின் SI அலகு மீ3
1 மி.மீ3 = 1 மைக்ரோ லிட்டர்
1 செ.மீ3 = 1 மில்லி லிட்டர்
1 மீ3 = 1 கிலோலிட்டர்
32. முற்காலத்தில் மக்கள் பகல் நேரத்தை கணக்கிட மணல் கடிகாரம் மற்றும் சூரியக்கடிகாரத்தைப் பயன்படுத்தி நேரத்தை அளவிட்டனர். தரையில் நடப்பட்ட ஒரு குச்சியின் நிழலினைக் கொண்டு நேரத்தைக் கணக்கிட முடியும். ஒரு சிறிய துளை உள்ள பாத்திரத்தைக் கொண்டு காலத்தைக் கணக்கிட்டனர். நீர் நிரம்பிய ஒரு பெரிய கலனில், துளையுள்ள இப்பாத்திரத்தை வைத்து அது மூழ்கும் நேரத்தைக் கணக்கிட்டனர். பின் இதனைக் கணக்கிடும் கருவியாகப் பயன்படுத்தினர். மேற்கண்ட கடிகாரங்கள் நேரத்தைத் தோராயமாக அளவிட உதவின. நவீன காலத்தில் மின்னணு கடிகாரங்கள், நிறுத்துக் கடிகாரம் போன்ற உபகரணங்கள் நேரத்தைத் துல்லியமாகக் கணக்கிட உதவுகின்றன.
33. பூமியின் பரப்பில் எடை என்பது நிறைக்கு நேர்தகவில் இருக்கும். பூமியை விட நிலவில் ஈர்ப்பு விசை குறைவு என்ற போதிலும் இரண்டிலும் நிறை சமமாகவே இருக்கும். ஆனால் எடை குறையும். நிலவில் ஈர்ப்புவிசை புவியைபோல ஆறில் ஒரு பங்கு தான். ஆகவே நிலவில் பொருளின் எடை என்பது பூமியில் உள்ள எடையில் ஆறில் ஒரு பங்கு ஆகும்.
34. ஓடோமீட்டர் என்பது தானியங்கி வாகனங்கள் கடக்கும் தொலைவைக் கணக்கிடுவதற்கு பயன்படுத்தப்படும் ஒரு கருவியாகும்.
35. மெட்ரிக் முறை அலகுகள் அல்லது திட்ட அலகுகள், 1790ல் ஃபிரெஞ்சுக்காரர்களால் உருவாக்கப்பட்டது.
36. நீளத்தை அளக்கத் தற்காலத்தில் பயன்படும் அளவுகோல், பதினாறாம் (16) நூற்றாண்டில் வில்லியம் பெட்வெல் என்ற அறிவியல் அறிஞரால் கண்டுபிடிக்கப்பட்டது.
37. ஃபிரான்ஸ் நாட்டின் தலைநகர் பாரீஸில் உள்ள எடைகள் மற்றும் அளவீடுகளுக்கான அனைத்துலக நிறுவனத்தில் பிளாட்டினம் - இரிடியம் உலோகக் கலவையிலான ஒரு படித்தர மீட்டர் கம்பி ஒன்று வைக்கப்பட்டுள்ளது. இந்த மீட்டர் கம்பியின் நகல் ஒன்று டில்லியில் உள்ள தேசிய இயற்பியல் ஆய்வகத்தில் வைக்கப்பட்டுள்ளது.
38. 1 கிலோகிராம் என்பது ஃபிரான்ஸில் உள்ள செவ்ரெஸ் என்ற இடத்தில் சர்வதேச எடைகள் மற்றும் அளவீடுகளுக்கான அனைத்துலக நிறுவனத்தால் 1889ல் நிறுவப்பட்ட, பிளாட்டினம்-இரிடியம் உலோகக் கலவையால் ஆன ஒரு உலோக தண்டின் நிறைக்கு சமம்.
LINE BY LINE NOTES FOR ENGLISH MEDIUM STUDENTS
- The comparison of unknown quantities with some known quantities is known as measurement.
- Measurement of a quantity has two parts: a number and its unit.
- Distance between one end and the other desired end is called as length
- The standard unit of length is metre. It is represented by letter 'm'
- Very small length can be measured in mm and cm.
- Large length can be measured in metre and kilometre
- The sake of uniformity, scientists all over the world have adopted a common set of units to express measurements. This system is called as the International System of units or SI units. Image screenshot
- Parallax is a displacement or difference in the apparent position of an object viewed along two different lines of sight.
- Area is obtained by using two lengths.
- Area = Length × Breadth.
- Volume is a derived quantity and it can be measured from measuring lengths.
- volume of the box = l × b × h
- Liquids take the shape of the container in which they are kept.
- Graduated cylinders, beakers, pipettes and burettes are available for measuring exact volumes of liquids.
- The volume of liquid is usually measured in litres.
- volume is the space occupied by an object.
- 1ml = 1 cubic cm
- Gases expand to fill the container into which they are placed.
- When you compress, a gas you can make the same gas to occupy lesser space.
- SI unit for Volume of solid is cubic metre
- Liquids and gases are usually measured in litres
- Liquids and gases are also can be measured in m3 or cubic metre.
- While using ruler, the accurate measurement can be arrived by avoiding three types of possible errors.
- Volume of irregular objects can be measured by water displacement method.
- Electronic balance is an instrument to provide accurate measurement of mass correct up to milligram.
- The weight is directly proportional to the mass on earth's surface. On moon where the gravitational force is lesser than earth, the weight will reduce but the mass will remain the same. The moon’s gravitational pull is one sixth of the earth’s pull. Thus objects weigh six times lighter on the Moon than on the Earth.
- Mass is the measure of the amount of matter in an object. Weight is the gravitational pull experienced by the mass.
- The SI unit of mass is kilogram. It is represented by the ‘kg’.
- Bigger weights are measured in tonne or Metric Tonne.
- A beam balance works by comparing the mass of an object to that of known mass (called a standard mass)
- An electronic balance is a device used to find accurate measurements of weight.
- An electronic balance is used very commonly in laboratories for weighing chemicals to ensure a precise measurement of those chemicals for use in various experiments.
- In earlier days people used sand clock and sundial to measure the passage of time during the day. The shadow cast by a stick can be used to estimate time. One can also use a vessel with a small hole for computing time. Take a vessel or bottle with a small hole in it and fill it with water. The time taken for water to drain can also be used as a measuring device. These are rough methods for counting passage of time. We can use electronic clock, stopwatch and other instruments to count even smaller durations of time.
- An odometer is a device used for indicating distance travelled by an automobile.
- The metric system or standard set of units was created by the French in 1790.
- A ruler or scale, used now a days to measure length was invented by a William Bedwell in 16th century.
- A standard metre rod made of an alloy of platinum and iridium is placed at the Bureau of weights and measures in Paris. National Physical Laboratory in Delhi has a copy of this metre rod.
- One kilogram is equal to the mass of a certain bar of platinum-iridium alloy that has been kept since 1889 at the International Bureau of Weights and Measures in Sèvres, France.
SI unit for length is Metre SI unit for mass is Kilogram SI unit for time is Second SI unit of area of surface is m2 SI unit of volume of solid is m3 1 m3 = 1 kilolitre (kl or kL) 1cm3 = 1 millilitre (ml or mL) 1mm3= 1 microlitre (µl or µL) 1000 milligram = 1 gram 1000 gram = 1 kilogram 1000 kilogram = 1 tonne 1 cm = 10 mm 1 m = 100 cm 1 km = 1000 m

டிஎன்பிஎஸ்சி தேர்வுக்கு தேவையான சில முக்கியமான இலவச தேர்வுகளின் லிங்க்குகள்
1. 20 Questions test series – Test 12- http://tpnkalvi.in/online-test/free-tests/20-questions-test-series-test-12/
2. 20 Questions test series – Test 11 - http://tpnkalvi.in/online-test/free-tests/20-questions-test-series-test-11/
3. 20 Questions test series – Test 10 - http://tpnkalvi.in/online-test/free-tests/20-questions-test-series-test-10/
4. 20 Questions test series – Test 9- http://tpnkalvi.in/online-test/free-tests/20-questions-test-series-test-9/
5. 20 Questions test series – Test 8- http://tpnkalvi.in/online-test/free-tests/20-questions-test-series-test-8/
6. 20 Questions test series – Test 7- http://tpnkalvi.in/online-test/free-tests/20-questions-test-series-test-7/
7. 20 Questions test series – Test 6 - http://tpnkalvi.in/online-test/free-tests/20-questions-test-series-test-6/
8. 20 Questions test series – Test 5 - http://tpnkalvi.in/online-test/free-tests/20-questions-test-series-test-5/
9. 20 Questions test series – Test 4 - http://tpnkalvi.in/online-test/free-tests/20-questions-test-series-test-4/
10. 20 Questions test series – Test 3 - http://tpnkalvi.in/online-test/free-tests/20-questions-test-series-test-3/
11. 20 Questions test series – Test 2 - http://tpnkalvi.in/online-test/free-tests/20-questions-test-series-test-2/
12. 20 Questions test series – Test 1 - http://tpnkalvi.in/online-test/free-tests/20-questions-test-series-test-1/




1 thought on “வரி வரியாகப் படித்து எடுக்கப்பட்ட கேள்விகள் – ஆறாம் வகுப்பு – அறிவியல்- இயல் 1”