பாடத் தலைப்பு : நம்மைச் சுற்றியுள்ள பருப்பொருட்கள் Matter around us
PDF டவுன்லோட் செய்ய : இந்த குறிப்புகள் அனைத்தையும் PDF வடிவில் டவுன்லோட் செய்துகொள்ள விரும்புபவர்கள், கீழே உள்ள தேர்வை ATTEND செய்யவும். தேர்வை முடிக்கும் பொழுது உங்களுடைய மதிப்பெண்ணுடன் PDF டவுன்லோட் செய்வதற்கான லிங்க்கும் காட்டப்படும். அதனைக் கிளிக் செய்து PDF டவுன்லோட் செய்து கொள்ளவும்.
இந்த இயலில் மொத்தம் 100 குறிப்புகளும் அவற்றைக் கொண்டு உருவாக்கப்பட்ட 40 கேள்விகளும் உள்ளன.
இந்தத் தேர்வு குறிப்புகள் குறித்த உங்களின் கருத்துக்களை கீழே உள்ள கமெண்ட் பாக்ஸில் தெரிவிக்கவும்
தேர்வு - கேள்விகளின் எண்ணிக்கை 40
வாழ்த்துகள். நீங்கள் இந்தத் தேர்வில் தேர்ச்சி பெற்றுள்ளீர் மீண்டும் இதே தேர்வினை எழுதுவதற்கு கீழே கிளிக் செய்யவும் அடுத்த தேர்விற்கு செல்ல கீழே கிளிக் செய்யவும் இந்தக் கேள்விகள் அனைத்தையும் PDF வடிவில் டவுன்லோட் செய்து கொள்ள விரும்புபவர்கள் கீழே கிளிக் செய்யவும் Tamil Medium Notes – Click here English Medium Notes – Click here இந்தக் கேள்விகள் உங்களுக்குப் பிடித்திருந்தால் எங்களைப் பாராட்டுவதற்கு கீழே உள்ள ஏதேனும் ஒரு விளம்பரத்தைக் கிளிக் செய்யவும். நீங்கள் இந்தத் தேர்வில் தேர்ச்சி பெறுவதற்கான மதிப்பெண்களைப் பெறவில்லை. மீண்டும் இதே தேர்வினை எழுதுவதற்கு கீழே கிளிக் செய்யவும் அடுத்த தேர்விற்கு செல்ல கீழே கிளிக் செய்யவும் இந்தக் கேள்விகள் அனைத்தையும் PDF வடிவில் டவுன்லோட் செய்து கொள்ள விரும்புபவர்கள் கீழே கிளிக் செய்யவும் Tamil Medium Notes – Click here English Medium Notes – Click here இந்தக் கேள்விகள் உங்களுக்குப் பிடித்திருந்தால் எங்களைப் பாராட்டுவதற்கு கீழே உள்ள ஏதேனும் ஒரு விளம்பரத்தைக் கிளிக் செய்யவும்.
click to copy shortcodeResults
#1. கிடைக்கும் இடத்தை நிரப்ப, பரவும் துகள்களின் தன்மை எவ்வாறு அழைக்கப்படுகிறது the tendency of particles to spread out in order to occupy the available space is
#2. திண்மங்கள் பற்றிய பின்வரும் கருத்துகளில் தவறானது எது Which of the following statements about solids is incorrect?
#3. திரவங்கள் பற்றிய பின்வரும் கருத்துகளில் தவறானது எது Which of the following statements about liquids is incorrect?
#4. வாயுக்கள் பற்றிய பின்வரும் கருத்துகளில் எது தவறானது Which of the following statements about gases is incorrect?
#5. எந்த தனிமத்தின் தூய்மை காரட் என்ற அலகால் குறிப்பிடப்படுகிறது Purity of _________ is expressed in the terms of carat
தேர்வு எழுதி முடிக்கும் பொழுது உங்களுடைய மதிப்பெண் மற்றும் PDF டவுன்லோட் செய்வதற்கான லிங்க் காட்டப்படும்
எங்கள் இணையதளத்தில் 6-ஆம் வகுப்பு முதல் 12-ஆம் வகுப்பு வரை உள்ள அனைத்து பாடங்களுக்குமான ஒரு வரி குறிப்புகள் அனைத்தும் பாடவாரியாக பதிவேற்றம் செய்யப்பட்டுள்ளது.
ஒவ்வொரு பாடத்திலிருந்தும் எடுக்கப்பட்ட குறிப்புகளை கொண்டு தயாரிக்கப்பட்ட தேர்வும் (TEST) கீழே கொடுக்கப்பட்டுள்ளது. குறிப்புகள் அனைத்தையும் படித்துவிட்டு அந்த தேர்வை எழுதிப் பார்க்கும் வசதியும் அளிக்கப்பட்டுள்ளது.
ஒருவரி வினாக்கள் அனைத்தும் பாடப்புத்தகத்தை வரி வரியாகப் படித்து எடுக்கப்பட்டதாகும்.
இந்தத் தொகுப்பில் உள்ள அனைத்து வினாக்களையும் நீங்கள் முறையாக பயிற்சி செய்தாலே தமிழகத்தில் நடைபெறும் அனைத்து வகையான போட்டித் தேர்வுகளிலும் வெற்றி பெறலாம்.
இது போன்று அனைத்து பாடங்களுக்குமான, வரி வரியாகப் படித்து எடுக்கப்பட்ட வினாக்களை பெற கீழே உள்ள டெலிகிராம்/ வாட்சப் குரூப்பில் இணைந்து கொள்ளவும்.
Telegram : https://t.me/THAMIZHPRIYANKALVI1
Whatsapp : https://chat.whatsapp.com/CAJ20fhIAwEHEmeagezQBS
youtube channel : https://www.youtube.com/c/ThamizhpriyanKalvi
Website: http://tpnkalvi.in/
வரி வரியாகப் படித்து எடுக்கப்பட்ட ஒரு வரி குறிப்புகள்
- பருப்பொருள் என்பது எடை உள்ளதும் இடத்தை அடைத்துக் கொள்வதுமாகும்.
- பருப்பொருட்கள் மூன்று நிலைகளில் காணப்படுகிறது. அவை திண்மம், நீர்மம் மற்றும் வாயு ஆகும்.
- எல்லா பருப்பொருள்களும் அணுக்களாலானதாகும்.
- அணுக்கள் பருப்பொருளின் மிகச் சிறிய துகள் ஆகும்.
- அணுக்கள் மிகச்சிறியவை,அணுக்களை நம்முடைய கண்கள் மற்றும் உருப்பெருக்கியினால் கூட பார்க்கமுடியாது.
- மின்சாரத்தின் மூலம் இயங்கும் எலக்ட்ரான் நுட்ப உருப்பெருக்கி மற்றும் ஊடுபுழை நுட்ப எலக்ட்ரான் கருவி போன்றவை அணுக்களின் அமைப்பைக் கண்டறியப் பயன்படுத்தப்படுகிறது.
- ஒரு மில்லியன் - 10,00,000
- திண்ம, திரவ மற்றும் வாயு நிலைகளைத் தவிர்த்து மேலும் இரண்டு நிலைகள் உள்ளன. அவை பிளாஸ்மா மற்றும் போஸ் - ஐன்ஸ்டீன் சுருக்கம் ஆகும்.
- பிளாஸ்மா நிலை என்பது பூமியில் உள்ள பருப்பொருளின் பொதுவான நிலை அல்ல. ஆனால், அது அண்டத்தில் கூடுதலாகக் காணப்படும் ஒரு பொதுவான நிலையாகும். எடுத்துக்காட்டாக சூரியனும் நட்சத்திர மண்டலமும் சேர்ந்த கலப்பு பிளாஸ்மா நிலை ஆகும்.
- போஸ் - ஜன்ஸ்ட்டீன் சுருக்கம் என்பது மிகக்குறைவான தட்பவெட்ப நிலையில் காணப்படும் வாயு நிலை போன்ற பருப்பொருள்களின் நிலை ஆகும்.
- போஸ் - ஜன்ஸ்ட்டீன் சுருக்கம் 1925ல் கணிக்கப்பட்டு, 1995 ல் உறுதி செய்யப்பட்டது .
- நிறையுள்ள மற்றும் இடத்தை அடைத்துக் கொள்பவை பருப்பொருள் ஆகும்.
- இந்தியாவின் கானடா என்ற தத்துவமேதையும், கிரேக்க தத்துவமேதை டெமாக்ரட்டிஸ்சும் பருப்பொருள் பற்றிய ஒத்த கருத்துக்களை கூறினர்.
- கானடா மற்றும் டெமாக்ரட்டிஸ் கூற்றுப்படி: நம்மால் முடிவற்ற நிலைக்குப் போக முடியாது என்பது இல்லை.
- பருப்பொருளில் உள்ள மிகச் சிறிய துகள்களே அணுக்கள் அல்லது மூலக்கூறுகள் என அழைக்கப்படுகிறது.
- பருப்பொருளில் உள்ள துகள்கள் மிகமிகச் சிறியவை. மேலும் அவை சக்தி வாய்ந்த, நுண்ணோக்கியால் கூடப் பார்க்க முடியாதவை ஆகும்.
- ஒரு துளி நீரில் ஏறக்குறைய 1021 நீர் துகள்கள் அடங்கியுள்ளது.
- பருப்பொருளின் துகள்களுக்கு இடையே அதிக இடைவெளி உள்ளது. இது வெவ்வேறு பருப்பொருளுக்கு வெவ்வேறாக இருக்கும்.
- சர்க்கரையை நீரில் கரைக்கும் பொழுது நீரின் துகள்களுக்கு இடையில் இடைவெளி உள்ளது. சர்க்கரைத் துகள்கள் அந்த இடைவெளிகளை நிரப்புகின்றன.
- பருப்பொருளின் துகள்களுக்கு இடையே ஈர்ப்பு விசை உள்ளது. இவ்விசையே துகள்களை பிணைக்கிறது. இத்தகைய ஈர்ப்பு விசை பருப்பொருளுக்கு, பருப்பொருள் மாறுபடுகிறது.
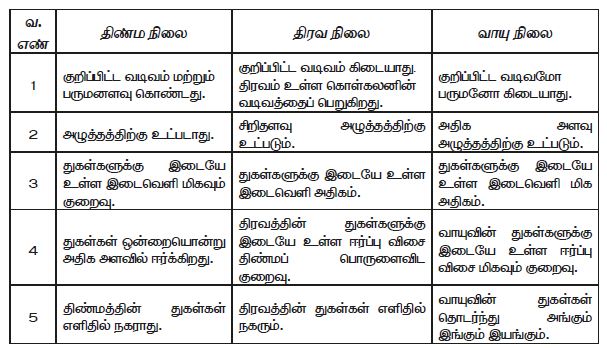
- இயற்பியல் நிலை அடிப்படையில் பருப்பொருள்களை திண்மம், திரவம் மற்றும் வாயு என பண்புகளின் அடிப்படையில் மூன்று வகையாகப் பிரிக்கலாம். இவையே பொருள்களின் இயற்பியல் நிலைகள் என அழைக்கப்படுகிறது.
- திண்மத்திற்கு என கொள்கலன் தேவையில்லை. அது எங்கிருந்தாலும் நிலையானது. ஏனெனில் அதன் துகள்கள் நெருக்கமாக அமைந்து குறிப்பிட்ட வடிவத்தைத் தருகிறது. எனவே சாதாரணமாக அதன் வடிவம் மாறாது.
- திரவத்தில் அணுக்களுக்கு இடையே இடைவெளி இருப்பதால், பொருட்கள் உள்ளே செல்ல அனுமதிக்கின்றன.
- திரவங்கள் புவி ஈர்ப்பு விளைவினால் அதிகம் ஈர்க்கப்படுகிறது.
- திரவத்தைச் சுற்றி புவிஈர்ப்பு விசை செயல்படுவதால் அதன் மூலக்கூறுகள் எப்போதும் இயங்கிக் கொண்டேயிருக்கும்.
- வாயு அணுக்கள் நீண்ட தூரத்திற்கு பரவுகிறது. பொருட்களால் எவ்வித தடையுமின்றி அதனுள் செல்ல இயலும். புவிஈர்ப்பு விளைவால் பாதிக்கப்படுவதில்லை
- வாயுக்கள் ஒரு இடத்தில் நிற்காமல் பரவிக்கொண்டே இருக்கும்.
- வாயுக்கள் மற்றும் திரவங்களின் துகள்கள் நகருவதால் மணம் பரவுகிறது.
- திரவத் துகள்களை விட வாயுத்துகள்கள் எளிதில் நகருகின்றது.
- விரவுதல் என்பது கிடைக்கும் இடத்தை நிரப்பப் பரவும் துகள்களின் தன்மை ஆகும்.
- இடம் முழுவதும் துகள்கள் பரவும் அல்லது விரவும் தன்மையே விரவுதல் எனப்படும்.
- திண்மங்களில் உள்ள துகள்கள் நகர இயலாநிலையில் உள்ளது. எனவே, அவை திரவம் அல்லது வாயுக்களைப் போல பரவாது.
- பாய்மங்களில் துகள்கள் இயக்கத்தில் உள்ளது, எனவே மை துகள்கள் மற்றும் புகைத் துகள்கள் அங்கும் இங்கும் விரவுகிறது.
- ஒரு திரவத்தை வைக்க கொள்கலன் தேவைப்படுகிறது. எனவே, அது கொள்கலனின் வடிவத்தைப் பெறுகிறது.
- திரவத் துகள்கள் ஒன்றோடொன்று ஒட்டுவதாலும், நழுவும் தன்மை கொண்டதாலும் கொள்கலனின் வடிவத்தைப் பெறுகிறது.
- வாயுக்கள் நீர்மமாக மாற்றப்படுவதற்கு “வாயுக்கள் நீர்மமாதல்" என்று பெயர்.
- வாயு மூலக்கூறுகள் அதிக அழுத்தம் மற்றும் குறைந்த வெப்பநிலையில் மூலக்கூறுகள் நெருக்கமாக அமைந்து, ஆற்றல் குறைக்கப்பட்டு வாயுக்கள் நீர்மமாக மாற்றப்படுகிறது
- திண்மம் மற்றும் திரவங்களை ஒப்பிடும் போது வாயுக்கள் அதிக அழுத்தத்திற்கு உட்படும்.
- ஒரு தூய பொருள் என்பது ஒரே தன்மையான துகள்களால் மட்டுமே ஆனது.
- தூய பொருள்கள் தனிமங்களாகவோ அல்லது சேர்மங்களாகவோ இருக்கலாம்.
- ஒரு தனிமம் என்பது சிறிய துகள்களாலான அணுக்களால் ஆனது.
- ஒரு மூலக்கூறு என்பது இரண்டு அல்லது அதற்கு மேற்பட்ட அணுக்களின் சேர்க்கையாகும்.
- ஒரு சேர்மம் என்பது இரண்டு அல்லது அதற்கு மேற்பட்ட தனிமங்கள் இணையும் வேதியியல் சேர்க்கையாகும்.
- தங்கத்தின் தூய்மை 'காரட்' என்ற அலகால் குறிப்பிடப்படுகிறது.
- 24 காரட் தங்கம் என்பது தூய நிலையில் உள்ள தங்கமாகக் கருதப்படுகிறது.
- ஆக்ஸிஜன், நைட்ரஜன், கார்பன் டை ஆக்ஸைடு, நீராவி, மந்த வாயுக்கள் மற்றும் பிறவற்றை தன்னுள் கொண்டதால் காற்று என்பது ஒரு கலவையாகும்.
- நீர், புரதம், கொழுப்பு மற்றும் பிற பொருள்களை தன்னுள் கொண்டதால் பாலும் ஒரு கலவையாகும்.
- கலவை என்பது அதில் அடங்கியுள்ள பகுதிப்பொருட்களின் அளவு நிலையான விகிதத்தில் இருக்க வேண்டும் என்கிற அவசியமில்லை.
- தனிமங்களின் வேதியியல் அடிப்படையிலான சேர்க்கையில் உருவாவது சேர்மம் என்று அறியப்படுகிறது.
- கலவைகள் உருவாவது என்பது பின்வரும் இயற்பியல் சேர்க்கை: அ)இரண்டு அல்லது இரண்டிற்கு மேற்பட்ட தனிமங்களை இணைத்தல் எ.கா : 22 கேரட் தங்கத்தில் உள்ள தங்கம் மற்றும் தாமிரம், தங்கம் மற்றும் காட்மியம் கலவைகள்.ஆ) இரண்டு அல்லது இரண்டிற்கு மேற்பட்ட சேர்மங்களை இணைத்தல் ௭.கா சோடாவில் உள்ள நீர், கார்பன் டை ஆக்ஸைடு, நிற மூட்டி, இனிப்பு.இ) ஒரு தனிமம் மற்றும் ஒரு சேர்மத்தினை இணைத்தல். அயோடின் டிஞ்சரில் காணப்படும் ஆல்கஹாலிலுள்ள அயோடின்.
- ஒரு கலவை என்பது ஒன்றுக்கு மேற்பட்ட ஒரே தன்மையான துகள்களைக் கொண்ட தூய்மையற்ற பொருளாகும்.
- கலவையின் பகுதிப் பொருட்கள் எந்த விகிதத்திலும் கலக்கப்பட்டு இருக்கும்.
- உலோகங்கள் பூமியின் மேற்பரப்பில் தாதுக்களாக அமைந்து உள்ளது.
- தூய உலோகத்தினை நாம் பெற வேண்டும் எனில், தாதுக்களை பலபடிகளை உள்ளடக்கிய செயல்முறைகளைப் பின்பற்றி பிரித்தெடுக்க வேண்டும்.
- ஒரு கலவையில் இருந்து அவற்றின் பல பகுதிப் பொருட்களைத் தனித்தனியே பிரித்து எடுக்கும் முறைக்கு பிரித்தெடுத்தல் என்று பெயர்.
- உண்மையான பண்புகள் மற்றும் பயன்பாட்டினை அறிய பொருட்களைப் பிரித்தல் அவசியம்.
- பிரித்தெடுத்தலின் அவசியங்கள்:
கலவைகளில் உள்ள மாசுக்களையும் தீங்கு விளைவிக்கும் பகுதிப் பொருட்களையும் நீக்குதல் (எ.கா) அரிசியில் உள்ள கற்களை நீக்குதல். - பயனளிக்கும் ஒரு பகுதிப் பொருளினை அதன் மற்ற பகுதிப் பொருட்களில் இருந்து தனித்தெடுத்தல் (எ.கா) பெட்ரோலியத்தில் இருந்து பெட்ரோல் பெறுதல்.
- ஒரு பொருளை மிகுந்த தூய நிலையில் பெறுதல் (எ.கா) தங்கச் சுரங்கத்தில் இருந்து தங்கம் பெறுதல்.
- பிரித்தெடுத்தலின் அவசியங்கள்:
- கலவையில் அடங்கியுள்ள பகுதிப் பொருள்களின் பண்புகளைப் பொருத்தே, கலவைகளைப் பிரித்தெடுக்கும் முறை தேர்வு செய்யப்படுகிறது.
- பொருட்களின் அளவு, வடிவம், இயற்பியல் தன்மை (திட, திரவ, வாயு) யினைப் பொருத்து பிரித்தெடுக்கும் முறை தேர்வு செய்யப்படுகிறது.
- வெவ்வேறு அளவுடைய திடப் பொருட்களைப் பிரித்தெடுக்கும் முறைக்கு சலித்தல் என்று பெயர். (எ.கா) மாவில் இருந்து தவிடூ நீக்குதல், மணலில் இருந்து சரளைக் கல்லை நீக்குதல்.
- துணி துவைக்கும் இயந்திரத்தில் மையவிலக்கு விசையைப் பயன்படுத்தி ஈர உடைகளில் இருந்து நீரினை வெளியேற்றும் முறைக்கு மைய விலக்கல் என்று பெயர்.
- மிகச் சிறிய அளவிலான கரையாத திடப்பொருட்களை திரவத்திலிருந்து பிரித்தடுக்க கடைதல் என்ற முறையினைக் கையாளலாம். (எ.கா) தயிரிலிருந்து வெண்ணைய் எடுத்தல்.
- தானியங்களை அவற்றின் தாவரத் தண்டுகளில் இருந்து பிரிப்பதற்காக விவசாயிகள் தண்டுகளை கடினமான பரப்பில் அடிக்கின்றனர். இம்முறைக்கு கதிரடித்தல் என்று பெயர்.
- இரும்புத் துகள் கொண்டுள்ள கலவையாக இருந்தால், இரும்பானது காந்தத்தால் கவரப்படும் என்ற பண்பினைப் பயன்படுத்தி காந்தத்தன்மையுடைய பொருட்களை காந்தத்தன்மை அற்ற பொருள்களில் இருந்து பிரிக்கலாம்.
- காந்ததத்தால் கவரப்படும் பொருள்களுக்கு காந்தத்தன்மையுடைய பொருள்கள் என்று பெயர்.
- காந்தத்தினைப் பயன்படுத்தி திண்மங்களைப் திடப் பொருள்களைப் பிரிக்கும் முறைக்கு காந்தப்பிரிப்பு முறை என்று பெயர்.
- ஒரு, கலவையில் கனமான பொருட்கள் இருப்பின் அவற்றைச் சிறிது நேரம் அசையாமல் வைக்கும் பொழுது எடை அதிகமான பொருட்கள் வண்டலாகத் தங்கி, மேலடுக்கில் தெளிந்த நீர்மம் கிடைக்கும். இம்முறைக்கு படியவைத்தல் என்று பெயர்.
- தெளிய வைத்து இறுத்தல் - இச்செயல் படியவைத்தலைத் தொடர்ந்து நிகழ்த்தப்படுகிறது. அடியில் தங்கிய வண்டலை பாதிக்காத வண்ணம் மேல் அடுக்கில் உள்ள நீரினை கவனமாக மற்றொரு கலனிற்கு மாற்றுதலே தெளிய வைத்து இறுத்தலாகும். அடியில் தங்கும் பகுதி வண்டல் என்றும், தெளிந்த நிலையில் உள்ள பகுதி தெளிந்த நீர் என்றும் அழைக்கப்படும்.
- ஒரு கலவையில் உள்ள களிமண், மணல் போன்ற கரையாத பொருள்களை வடிதாளைப் பயன்படுத்தி பிரித்தெடுக்கும் முறைக்கு வடிகட்டுதல் என்று பெயர்.
- பெரும்பாலான இல்லங்களில் நீரில் உள்ள மாசுக்களை நீக்குவதற்காகவும், நீரில் உள்ள நுண்கிருமிகளை புறஊதா கதிர்களைக் கொண்டு அழிப்பதற்காகவும் வணிக நீதியான நீர் வடிகட்டிகள் பயன்படுத்தப்படுகின்றன.
- எதிர் சவ்வூடு பரவல் என்ற முறையில், குடிப்பதற்கென நீரில் உள்ள மாசுக்கள் நீக்கப்பட்டு, சுத்திகரிக்கப்படுகிறது.
- வடிகட்டியைக் கடந்து கீழே இறங்கும் திரவத்திற்கு வடிநீர் என்றும், வடிதாளில் தங்கும் கரையாத பகுதிக்கு வண்டல் என்றும் பெயர்.
- உணவுப்பொருட்களில் தேவையற்ற பொருட்களோ அல்லது தீங்கு விளைவிக்கும் பொருட்களோ காணப்படும். இதற்கு உணவுக்கலப்படம் என்று பெயர். கவனமின்மையாலும், சரியாகக் கையாளாத காரணங்களாலும் உணவுக் கலப்படம் ஏற்படலாம்.
- கலப்படம் செய்யப்பட்ட பொருள்கள், தூய பொருள்களின் உண்மைப் பண்புகளைப் பெற்றிருக்காது.
- பருப்பொருள் என்பது நிறை உடையது மற்றும் இடத்தை அடைத்துக் கொள்வது.
- எல்லா பருப்பொருள்களும் மிகமிகச் சிறிய துகள்களால் ஆனவை
- இண்டு முக்கியப் பண்புகளின் அடிப்படையில் பருப்பொருளை திண்மம், திரவம் மற்றும் வாயு என வகைப்படுத்தலாம். அவை
அ) துகள்களின் அமைப்பை பொருத்து
ஆ) துகள்கள் ஒன்றையொன்று ஈர்க்கும் தன்மையைப் பொருத்து - துகள்களின் அமைப்பு மற்றும் துகள்களுக்கிடையே உள்ள ஈர்ப்பு விசையின் அடிப்படையில் திட, திரவ மற்றும் வாயுக்களின் பண்புகளை வேறுபடுத்தலாம்.
- ஒரு தூயப் பொருள் என்பது ஒரு தனிமத்தாலோ அல்லது ஒரு சேர்மத்தாலோ ஆன ஒரே மாதிரியான துகள்களைக் கொண்டதாகும்.
- ஒரு கலவை என்பது இரண்டு பகுதிப் பொருள்களையோ அல்லது அதற்கு மேற்பட்ட பகுதிப் பொருள்களையோ எந்த ஒரு விகிதத்திலும் கலந்து உருவாக்கப்பட்ட தூய்மையற்ற பொருளாகும்.
- கலவையைப் பிரித்தல் - தீங்கு விளைவிக்கும் பகுதிப் பொருள்களை நீக்கவும், தேவைப்படும் பகுதிப்பொருளினைப் பெறவும், ஒரு பொருளினை மிகத் தூய நிலையில் பெறவும் நிகழ்த்தப்படுகிறது.
- ஒரு கலவையில் உள்ள பகுதிப் பொருள்களின் பண்புகளைப் பொறுத்தே அக்கலவையினைப் பிரித்தெடுக்கும் முறை நிர்ணயிக்கப்படுகிறது.
- கைகளால் தெரிந்தெடுத்தல் - குறைந்த அளவிலான கலவைகளில் குறிப்பிட்ட அளவும் பிரத்யேக வடிவமும் கொண்டு, கண்ணால் காணக்கூடியதும் எளிதில் கைகளால் தெரிந்து எடுக்கக் கூடியதுமான பகுதிப் பொருள்களைப் பிரித்தெடுக்கும் முறை
- தூற்றல் - கனமான பொருள்களில், மற்றும் தானியங்களில் கலந்துள்ள லேசான பொருள்களை நீக்கும் முறை
- காந்தப் பிரிப்பு முறை - காந்தத்தன்மை கொண்ட பொருள்களை காந்தத்தன்மையற்ற பொருள்களிலிருந்து பிரிக்கும் முறை
- வண்டலாக்குதல் - கனமான, கரையாத, திடப் பொருள்களை வண்டலாகப் படிய வைத்து அதனைப் பிரிக்கும் முறை (திண்ம - திரவக் கலவைகளைப் பிரிப்பதற்குப் பயன்படுகிறது.
- தெளியவைத்து இறுத்தல் - படிய வைத்து வண்டலைப் பாதிக்காத வண்ணம் தெளிந்த நீரை வெளியேற்றுதல்.
- வடிகட்டுதல் - கரையாத மிக நுண்ணிய திடப்பொருட்களை (வீழ்படிவு) அதன் நீர்மத்திலிருந்து இருந்து வடிதாளைப் பயன்படுத்தி பிரித்தெடுக்கும் முறை
- கலப்படம் - ஒத்த வடிவம் உடைய, தரம்குறைந்த பொருளை கலந்து ஒரு முதன்மைப் பொருளினைத் தூய்மையற்றதாக மாற்றுவது.
- ஒளி என்பது பருப்பொருளால் ஆனது அல்ல
- 400 மி.லி கொள்ளவு கொண்ட ஒரு கிண்ணத்தில் 200 மிலி நீர் ஊற்றப்படுகிறது. இப்போது நீரின் பருமன் 200 மி.லி
- தர்பூசணி பழத்தில் உள்ள விதைகளை கைகளால் தெரிந்தெடுத்தல் முறையில் நீக்கலாம்.
- அரிசி மற்றும் பருப்புகளில் கலந்துள்ள லேசான மாசுப் பொருள்களை புடைத்தல் முறையில் நீக்கலாம்.
- தூற்றுதல் என்ற செயலை நிகழ்த்த காற்று அவசியம் தேவைப்படுகிறது.
- திடப்பொருள் - நீர்மம் வகையான கலவையினை வடிகட்டுதல் முறையினால் பிரித்தெடுக்கலாம்.
- மனித உடல் எடையில் சுமார் 7-8% வரை இரத்தம் உள்ளது.
- இரத்தத்தின் முக்கியப் பணியானது உடலின் அனைத்து செல்களுக்கும் ஆக்ஸிஜன் மற்றும் சத்துக்களை கடத்துதல் ஆகும்.
- கார்பன்டை ஆக்ஸைடு, அம்மோனியா மற்றும் இதர கழிவுப் பொருள்களை வெளியேற்றுவதிலும், உடல் வெப்பநிலையைச் சீராக வைப்பதிலும், நோய் எதிர்ப்புசக்தியை நெறிப்படுத்துவதிலும் இரத்தம் பெரும் பங்கு வகிக்கிறது.
- இரத்தத்தில் 4,000க்கும் மேற்பட்ட பகுதிப் பொருள்கள் உள்ளன. அவற்றுள் இரத்த சிவப்பு அணுக்கள், இரத்த வெள்ளை அணுக்கள், இரத்தத்தட்டுகள், பிளாஸ்மா ஆகியவை நான்கு முக்கிய பகுதிகளாகும்.
- பிளாஸ்மா என்ற திரவத்திலேயே இரத்த சிவப்பு அணுக்கள், இரத்த வெள்ளை அணுக்கள், இரத்தத்தட்டுகள் ஆகியவை உள்ளன.
- இரத்தம் என்பது தூய பொருளல்ல; அது ஒரு கலவை.
LINE BY LINE NOTES FOR ENGLISH MEDIUM STUDENTS
- Matter is defined as anything that has mass and takes up space.
- Matter is found in three major states; solid, liquid and gas.
- All matter is made of atoms.
- Atoms are the smallest particle of matter.
- Atoms are so small that you cannot see them with your eyes or even with a standard microscope.
- Science has come up with a technology to identify structure of atoms Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) and Tunnelling Electron Microscope (TEM) which uses electricity to map atoms.
- 1 million = 1000000
- Besides solids, Liquid and gases there are two more states plasma and Bose – Einstein condensates.
- Plasma is not a common state of matter on Earth, but may be the most common state of matter in the universe. For example, stars including sun are covered in plasma.
- Bose – Einstein condensate is a gas – like state of matter that exists at extremely cold temperatures.
- Bose – Einstein condensate was predicted around 1925 and confirmed in 1995.
- Matter occupies space and has mass.
- In India a philosopher named Kanada and in Greece a philosopher named Democritus came to somewhat similar idea about matter.
- Kanada and Democritus said, No; we cannot go on endlessly.
- Tiny particles present in all matter are called as atoms or molecules.
- The particles in matter are extremely small and cannot be seen even with a powerful microscope.
- A drop of water contains about 1021 water particles.
- Particles of matter have a lot of space in between them. In different forms of matter this spacing will be different.
- Water particles have space between them, While adding sugar with water, sugar particles are occupying those spaces.
- Particles of matter attract each other. It is this attraction which keeps the particles together. This attractive force will be different for different forms of matter.
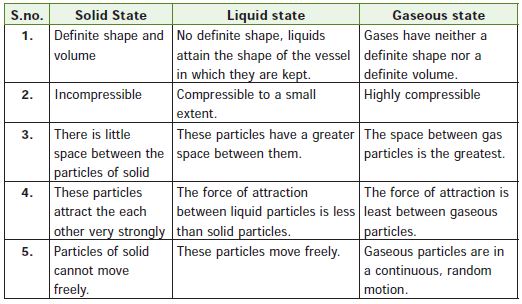
- Matter can be grouped into Solids, Liquids and Gases based on its characteristics. These are called the physical states of matter.
- A solid does not need a container; it stays where it is because its particles are tightly packed into a definite shape that, ordinarily, does not change.
- Liquid atoms are packed more loosely which allows things to be able to pass through it
- Liquid is effected by gravity more than anything.
- Liquids are always moving due to gravity around it.
- A gas atoms are spread out so far, you can walk through it without any restriction. Gas is not affected by gravity
- The gas's atoms never stop moving and it never stays in place.
- the particles of gases and liquids can move and that among gases more easily. We call this movement as diffusion.
- Diffusion is the tendency of particles to spread out in order to occupy the available space.
- Movement of particles is restricted in solids and they do not diffuse like liquids or gases.
- In fluids the particles are under motion and hence can push ink or smoke particles here and there.
- A liquid needs a container and takes the shape of a container because the particles slide past one another and keep moving.
- “Liquefaction of gases” is the process by which substances in their gaseous state are converted to the liquid state.
- When pressure on a gas is increased, its molecules comes closer together, and its temperature is reduced, which removes enough energy to make it change from the gaseous to the liquid state.
- gases are highly compressible as compared to liquids and solids.
- A pure substance is made up of only one kind of particles.
- Pure substances may be elements or compounds.
- An atom is the smallest particle that an element is made up of same kind of atoms.
- Molecule is the combination of two or more atom.
- Compound is the substance formed by the chemical combination of two or more element.
- Purity of gold is expressed in terms of ‘carat’.
- 24 carat gold is considered to be gold in its purest form.
- Air is a mixture because it contains Oxygen, Nitrogen, Carbon dioxide, water vapour, noble gases etc.
- Milk is a mixture of water, fat, protein etc.
- A mixture need not have a fixed proportion of components.
- When elements chemically combine they form compounds.
- mixture can be a physical combination of
- a) two or more elements. Example: 22 carat gold which is composed of gold and copper / gold and cadmium,
- b) two or more compounds. Example: aerated drink which is composed of carbon-di-oxide, water, sweetening and colouring agents,
- c) an element and compound. Example : Tincture of iodine which is composed of Iodine in alcohol.
- A Mixture is an impure substance and contains more than one kind of particles.
- In the mixture the components are mixed in any proportion.
- Metals occur in the form of ores under the earth’s crust.
- if we want to use a pure metal, we need to adopt a laborious process of extraction to separate the useful metal from the ore.
- The process by which the components of mixture are isolated and removed from each other to get pure substance is called separation.
- To get the original properties and uses of substance we need separation.
- Reasons to separate mixtures:when we need to remove impurities or harmful components from the mixtures (eg: stones from rice)
when the useful component has to be separated from other components (eg: petrol from petroleum)
when a substance has to be obtained in highly pure form (eg: gold from gold mines) - The choice of method of separation depends upon the properties of the components of the mixture.
- The separation method may be based on the particle’s size, shape or physical state – they may be solids, liquids or gases.
- Sieving is used when we have to separate solid particles of different sizes. Eg: bran from flour, sand from gravel etc.
- In washing machines centrifugal force is used to squeeze out dirt from clothes and the method is called centrifugation.
- When very fine insoluble solids have to be separated from a liquid as in butter from curds, Churning is performed.
- Farmers separate grains from their stalks by beating them so hard that the grains are separated from their stalks. This is called Threshing.
- In a mixture containing iron, the magnetic property of iron can be used to separate it from non- magnetic substances by using a magnet.
- Substances that are attracted to a magnet are called magnetic.
- Separating solids using a magnet is called magnetic separation.
- The settling down of heavier component of a mixture when allowed to remain undisturbed for some time is called sedimentation.
- Decantation process is done after sedimentation. The supernatant liquid is slowly poured out from the container without disturbing the sediment. The part that has settled down is called sediment. The water that is obtained after decantation is called the decantate
- The method of separating insoluble component (sand, mud etc.) from a mixture using a filter paper is called filtration.
- In most houses people use commercial water filter to remove not only the impurities but also to kill the harmful germs in water using UV rays.
- RO – a process of removing impurities from water to make it potable.
- The liquid which passes through the filter and comes down is called filtrate and the insoluble component left behind on the filter is called residue.
- Sometimes, things that we buy in the market are mixed with harmful and unwanted substances. This process is called adulteration. Food can also get adulterated due to carelessness or lack of proper handling.
- An adulterated substance will not indicate the true properties of the original substance.
- Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space.
- All matter is made up of extremely small particles.
- Matter is classified into solids, liquids and gases on the basis of two important factors .
a. The way the particles are arranged
b. The way the particles attract each other. - Difference between the properties of solids, liquids and gases is due to the difference in the arrangement of the particles and the nature of the attractive forces between them.
- A pure substance can be an element or a compound and is made up of only one kind of particles.
- A mixture is an impure substance containing two or more components physically mixed in any proportion.
- Separation of mixtures is done
1) to remove harmful components2) to obtain the useful component3) to obtain a substance in a highly pure form - Separation method to be adopted depends on the properties of the components.
- Handpicking – For smaller quantities containing particles reasonably large in size to be recognised can be picked by hand
- Winnowing – Adopted to separate lighter solids from heavier ones
- Magnetic separation – Used to separate magnetic substance from non-magnetic substance
- Sedimentation – Settling down of suspended, insoluble and heavy solid particles (used to separate solid – liquid mixtures)
- Decantation- Process of pouring out the clear supernatant liquid without disturbing the sediment
- Filtration –Process of separating insoluble solid particles (residue) from a liquid (filtrate) by using a filter paper.
- Adulteration – make impure by the addition of a foreign or inferior substance.
- light ray is not made of matter
- 200 ml of water is poured into a bowl of 400ml capacity. The volume of water now will be 200ml
- Seeds from water-melon can be removed by hand-picking method
- Lighter impurities like dust when mixed with rice or pulses can be removed by winnowing
- Air is essential to perform winnowing activity
- Filtration method is effective in separating solid-liquid mixture
- Blood constitutes about 7-8% of human body weight.
- Blood has the important function of transporting oxygen and nutrients to our cells and getting rid of carbon dioxide, ammonia, and other waste products, in immunity and also in regulating our body temperature.
- Blood is composed of more than 4,000 different kinds of components. Four of the most important ones are red cells, white cells, platelets, and plasma.
- Plasma is the liquid in which the red cells, white cells and platelets are present.
- Blood is not a pure substance but a mixture.
டிஎன்பிஎஸ்சி தேர்வுக்கு தேவையான சில முக்கியமான இலவச தேர்வுகளின் லிங்க்குகள்
1. 20 Questions test series – Test 12- http://tpnkalvi.in/online-test/free-tests/20-questions-test-series-test-12/
2. 20 Questions test series – Test 11 - http://tpnkalvi.in/online-test/free-tests/20-questions-test-series-test-11/
3. 20 Questions test series – Test 10 - http://tpnkalvi.in/online-test/free-tests/20-questions-test-series-test-10/
4. 20 Questions test series – Test 9- http://tpnkalvi.in/online-test/free-tests/20-questions-test-series-test-9/
5. 20 Questions test series – Test 8- http://tpnkalvi.in/online-test/free-tests/20-questions-test-series-test-8/
6. 20 Questions test series – Test 7- http://tpnkalvi.in/online-test/free-tests/20-questions-test-series-test-7/
7. 20 Questions test series – Test 6 - http://tpnkalvi.in/online-test/free-tests/20-questions-test-series-test-6/
8. 20 Questions test series – Test 5 - http://tpnkalvi.in/online-test/free-tests/20-questions-test-series-test-5/
9. 20 Questions test series – Test 4 - http://tpnkalvi.in/online-test/free-tests/20-questions-test-series-test-4/
10. 20 Questions test series – Test 3 - http://tpnkalvi.in/online-test/free-tests/20-questions-test-series-test-3/
11. 20 Questions test series – Test 2 - http://tpnkalvi.in/online-test/free-tests/20-questions-test-series-test-2/
12. 20 Questions test series – Test 1 - http://tpnkalvi.in/online-test/free-tests/20-questions-test-series-test-1/



